38
April 2020
thermodynamically efficient, which will result in lower
operating costs. The downside to this, however, is that
actions such as this can sometimes be undertaken at the
expense of adding additional equipment and complexity to
production. This will also have to be monitored. In other
areas, the production trains are becoming larger, which
results in lower production cost. Nevertheless, in this case
the cost of downtime becomes more expensive if the train
is unexpectedly down. Ultimately, the benefits of developing
technology in either case become much more significant if
the risks can be mitigated.
Regardless of the chosen course of development,
machine condition monitoring will play an even more
important role in ensuring uninterrupted reliable production
in future scenarios. Performance monitoring of machines is
already standard practice for many existing machines and
larger machine sizes present no monitoring obstacles.
Condition monitoring is already geared for these and other
future development requirements, based on past experience
of successfully dealing
with existing operation
and maintenance
challenges.
Asset
healthcare
challenges
today
Machines in an LNG plant,
especially those involved
in the liquefaction process,
are subject to extreme
operating conditions. The
thermal expansion of a
refrigerant compressor,
pump or liquid expander
between startup and full production at cryogenic
temperatures is intense, thereby subjecting the bearings
and other machine components to severe loads during
startup and shutdown. Even small variations in the
process can have significant effects on the overall
loading of the machines. As many machines are
operated at variable speeds and loads, this basically
renders calculated mean-time-before-failure values
for the machine components to spread out and be
unpredictable.
As in many other sectors of the petrochemical
industry, ensuring the reliable operation of these
machines is not a trivial task – especially when
considering the reduced numbers of maintenance staff
and specialists onsite at plants, and the increasingly
competitive nature of the industry.
Condition monitoring solutions
are evolving
Very few people in the LNG industry dispute the merits
of effective condition monitoring, but there is a wide
disparity on what constitutes an effective monitoring
solution. Some simply continue to use their legacy
system without being aware that condition monitoring
technology itself has evolved over the years.
However, it is now possible to detect developing
symptoms from a wider range of potential failure modes
earlier and more reliably than 10 years previously. In a
similar fashion, diagnostics have become more accurate in
assessing fault severity and establishing the need for
maintenance action within an accurate timeframe.
Advancing data science technology enables process data to
be more readily correlated with fault monitoring data, so
that diagnostics and root cause analysis can be performed
faster and more accurately. Automatic fault prognostics and
decision support become a reality after many years of
monitoring data has been accumulated and can now be
analysed by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning
(ML).
Case studies
Current condition monitoring technology provides early
healthcare awareness for all the critical machines and
much of the balance-of-plant to reduce downtime and
maintenance costs, while at the same time avoiding
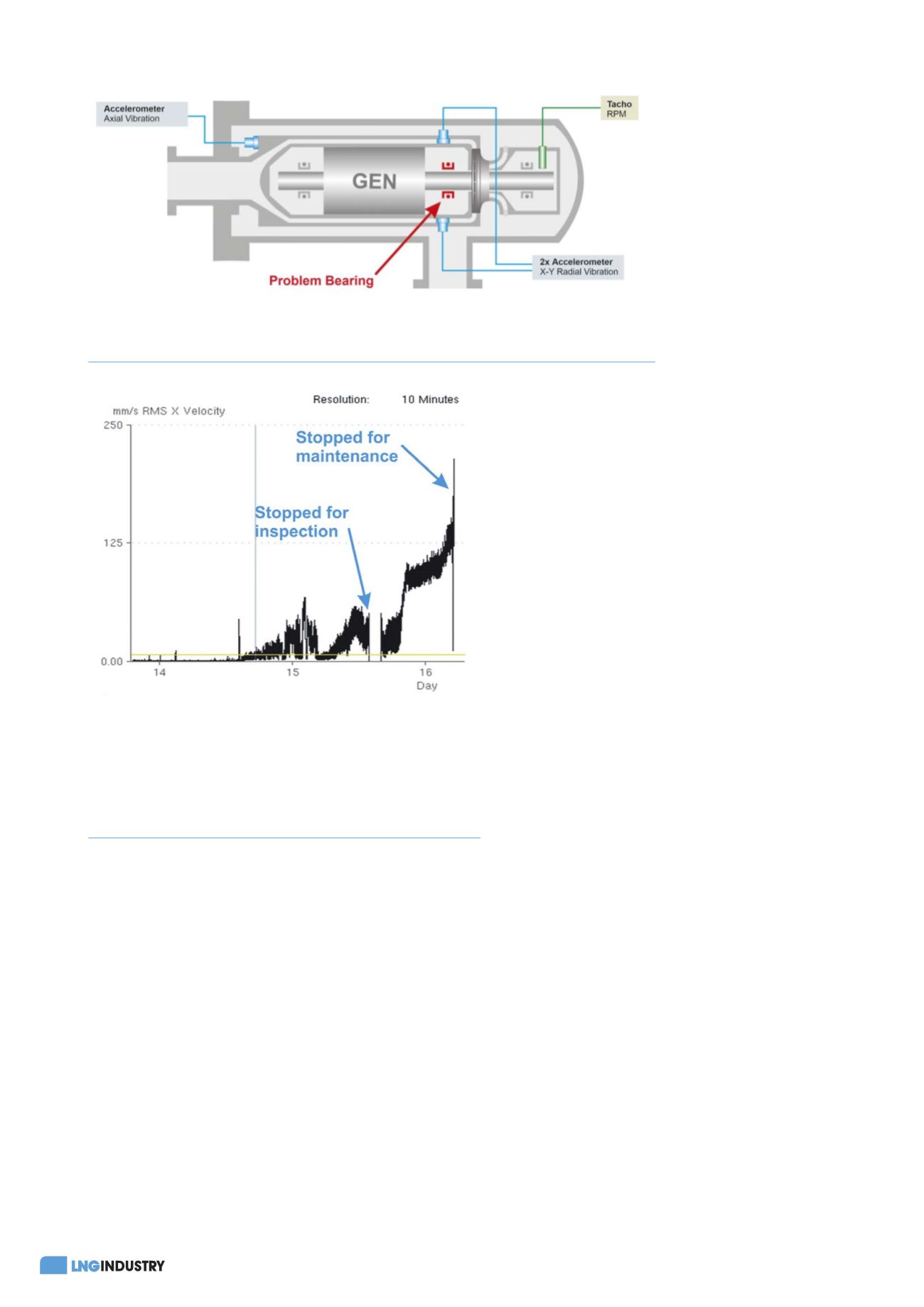
Figure 1.
Vibration sensor configuration of the liquid expander. The bearing where high
vibration was detected is shown in red.
Figure 2.
The vibration trend progressively increased after two
startups, so the liquid expander was shutdown for inspection. No
damage was found so it was started up again, but the vibration
continued to increase. Finally, it was shutdown for maintenance
and this time it was observed that the bearings showed signs of
damage.








